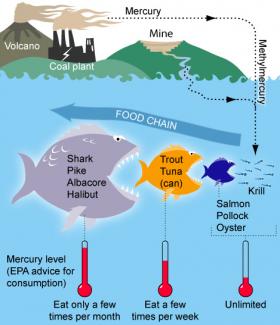
A global commitment to reduce health risks and environmental damage from mercury pollution came into effect last month (16 August), when the so-called Minamata Convention on Mercuryentered into force.
The 74 countries which have become parties to the convention so far — out of 128 that have signed — are now legally bound to take measures towards eliminating new sources of mercury, reducing its use, trade and emissions, and regulating disposal of the element.
“Upon entry into force parties are obliged to obey all obligations within the Convention, some immediately (like the ban on the opening of new mercury mines); others, in a few years – for example, the phaseout of the manufacture, import and export of mercury-added products takes effect in 2020,” says Sheila Longan of the Interim Secretariat of the Minamata Convention.
Continue reading at ENN affiliate, SciDev.Net
Image via Environmental Health Division - State of Alaska