That “archived” heat, currently trapped below the surface, has the potential to melt the region’s entire sea-ice pack if it reaches the surface, researchers say. The study appears online Aug. 29 in the journal Science Advances.
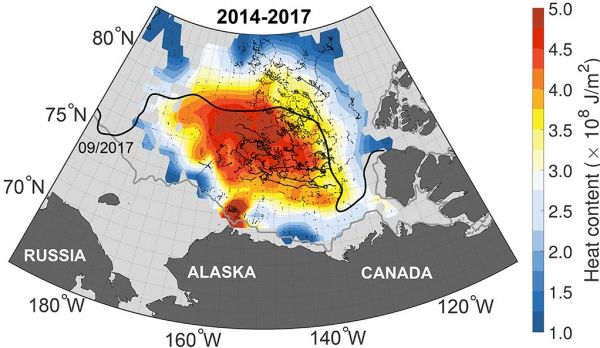
“We document a striking ocean warming in one of the main basins of the interior Arctic Ocean, the Canadian Basin,” said lead author Mary-Louise Timmermans, a professor of geology and geophysics at Yale University.
The upper ocean in the Canadian Basin has seen a two-fold increase in heat content over the past 30 years, the researchers said. They traced the source to waters hundreds of miles to the south, where reduced sea ice has left the surface ocean more exposed to summer solar warming. In turn, Arctic winds are driving the warmer water north, but below the surface waters.
Continue reading at Yale University
Image via Yale University