Multiple sclerosis is an autoimmune disease in which the body’s own immune system attacks and damages the protective coating around nerve cells. This coating is made up of myelin – a biological membrane of protein and fatty substances – which is why research efforts to find the disease’s target antigen have so far focused on the myelin membrane’s components. New findings made by the research group of Mireia Sospedra and Roland Martin from the University of Zurich’s Clinical Research Priority Program Multiple Sclerosis now suggest that it is worth broadening the research perspective to gain a better understanding of the pathological processes.
Inflammatory cascade
In the journal Science Translational Medicine, the scientists report that T cells – i.e. the immune cells responsible for pathological processes – react to a protein called GDP-L-fucose synthase. This enzyme is formed in human cells as well as in bacteria frequently found in the gastrointestinal flora of patients suffering from multiple sclerosis. “We believe that the immune cells are activated in the intestine and then migrate to the brain, where they cause an inflammatory cascade when they come across the human variant of their target antigen,” says Mireia Sospedra.
For the genetically defined subgroup of MS patients examined by the researchers, results show that gut microbiota could play a far greater role in the pathogenesis of the disease than previously assumed. Mireia Sospedra hopes that these findings can soon also be translated into therapy; she plans to test the immunoactive components of GDP-L-fucose synthase using an approach that the researchers have been pursuing for several years already.
Read more at University of Zurich
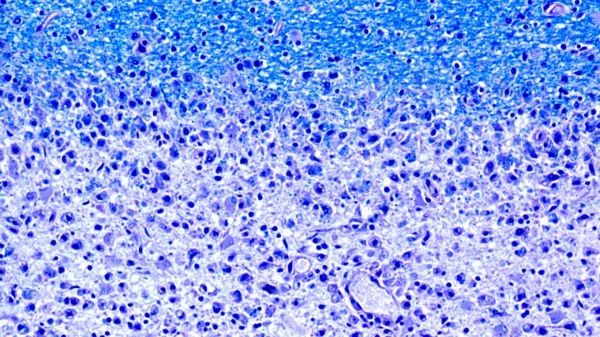
Image: Diminishing myelin sheaths: The damaged areas (at the bottom of the image) of the brains of MS patients lack myelin (at the top, in blue). (Image: Dr. med. Imke Metz, University of Göttingen, Germany) (Credit: Dr. med. Imke Metz, University of Göttingen, Germany)