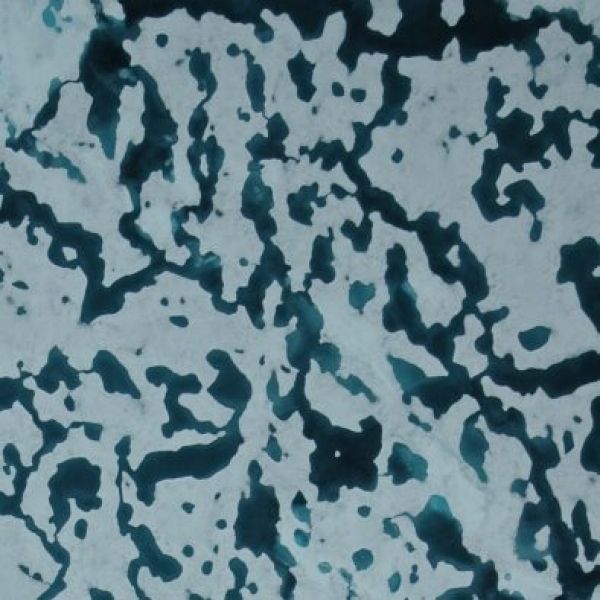
The Arctic is melting faster than we thought it would. In fact, Arctic ice extent is at a record low. When that happens—when a natural system behaves differently than scientists expect—it’s time to take another look at how we understand the system. University of Utah mathematician Ken Golden and atmospheric scientist Court Strong study the patterns formed by ponds of melting water atop the ice. The ponds are dark, while the ice is bright, meaning that the bigger the ponds, the darker the surface and the more solar energy it absorbs.
So, it’s more than a little important to know how the ice’s reflectivity, also called albedo, is changing. That’s a key component in understanding the balance between solar energy coming in and energy reflected out of the Arctic. Earlier work showed that the presence or absence of melt ponds in global climate models can have a dramatic effect on long term predictions of Arctic sea ice volume.
To model the melt ponds’ growth, Golden, Strong and their colleagues tweaked a nearly 100-year-old physics model, called the Ising model, that explains how a material may gain or lose magnetism by accounting for how atoms interact with each other and an applied magnetic field. In their model, they replaced the property of an atom’s magnetic spin (either up or down) with the property of frozen (white) or melted (blue) sea ice.
“The model captures the essential mechanism of pattern formation of Arctic melt ponds,” the researchers write, and replicates important characteristics of the variation in pond size and geometry. This work is the first to account for the basic physics of melt ponds and to produce realistic patterns that accurately demonstrate how melt water is distributed over the sea ice surface. The geometry of the melt water patterns determines both sea ice albedo and the amount of light that penetrates the ice, which significantly impacts the ecology of the upper ocean.
Read more at: University of Utah
Ponds of meltwater atop Arctic ice. (Photo credit: Don Perovich)