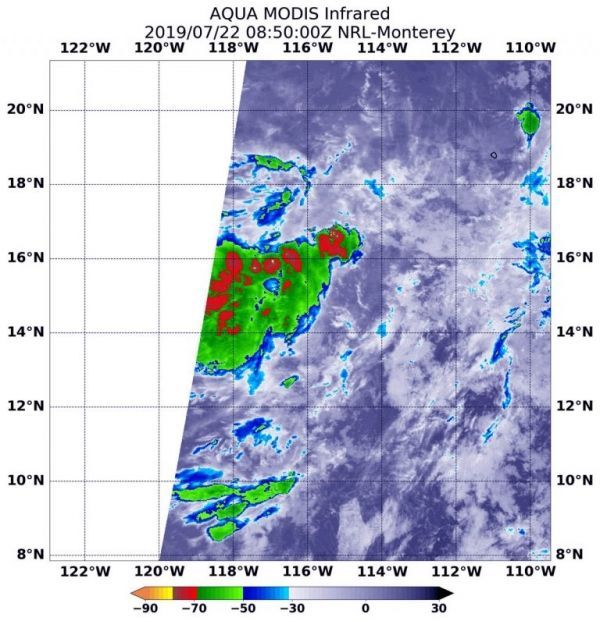
A new tropical depression formed in the Eastern Pacific Ocean, far enough away from the coast so that no coastal warnings are needed. Infrared imagery from NASA’s Aqua satellite shows that Tropical Depression 5E’s strongest storms were southwest of its center of circulation because of outside winds.
NASA’s Aqua satellite used infrared light to analyze the strength of storms and found the bulk of them in the southern quadrant. Infrared data provides temperature information, and the strongest thunderstorms that reach high into the atmosphere have the coldest cloud top temperatures.
On July 22 at 4:50 a.m. EDT (0850 UTC), the Moderate Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument that flies aboard NASA’s Aqua satellite gathered infrared data on Tropical Depression 5E. Strongest thunderstorms had cloud top temperatures as cold as minus 70 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 56.6 Celsius). Cloud top temperatures that cold indicate strong storms with the potential to generate heavy rainfall. Those strongest storms were southwest of the center of circulation because of vertical wind shear (winds blowing at different speeds at different levels of the atmosphere). The National Hurricane Center noted, “It appears that northeasterly shear is keeping much of the convection displaced to the west of the center of circulation.”
Read more at NASA / Goddard Space Flight Center
Image: On July 22 at 4:50 a.m. EDT (0850 UTC) the MODIS instrument that flies aboard NASA’s Aqua satellite showed strongest storms in Tropical Depression 5# were south of the elongated center where cloud top temperatures were as cold as minus 70 degrees Fahrenheit (red) (minus 56.6 Celsius). CREDIT: NASA/NRL