Hexagonal-boron nitride is tough, but Rice University scientists are making it easier to get along with.
Two-dimensional h-BN, an insulating material also known as “white graphene,” is four times stiffer than steel and an excellent conductor of heat, a benefit for composites that rely on it to enhance their properties.
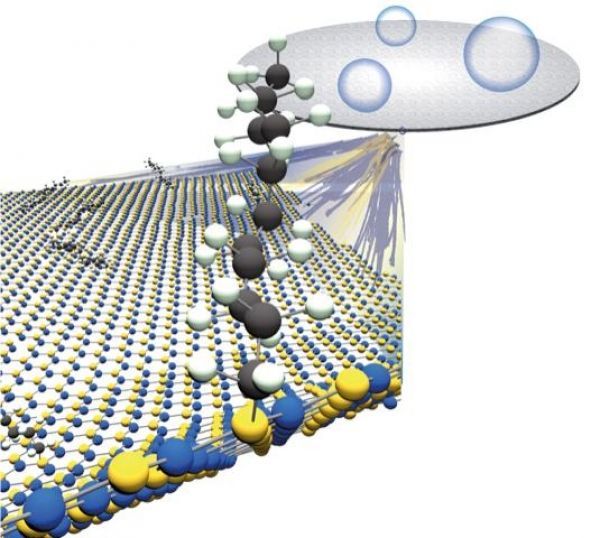
Those qualities also make h-BN hard to modify. Its tight hexagonal lattice of alternating boron and nitrogen atoms is highly resistant to change, unlike graphene and other 2D materials that can be easily modified — aka functionalized — with other elements.
The Rice lab of chemist Angel Martí has published a protocol to enhance h-BN with carbon chains. These turn the 2D tough guy into a material that retains its strength but is more amenable to bonding with polymers or other materials in composites.
Read more at: Rice University
Rice University scientists have made it much simpler to add carbon chains to hexagonal-boron nitride, a 2D material much stiffer than steel and an excellent conductor of heat. (Photo Credit: Illustration courtesy of the Angel Martí Group/Rice University)