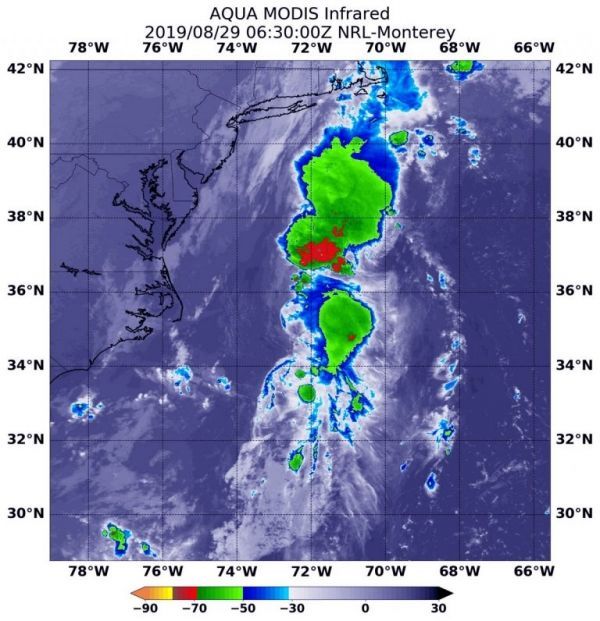
Former tropical depression Erin has made the transition into an extra-tropical system off the eastern coast of the U.S. Infrared imagery from NASA’s Aqua satellite provided temperature data on storms associated with Erin and the weather system it is merging with.
NOAA’s National Hurricane Center or NHC issued the final advisory on Erin on Aug. 29 at 5 a.m. EDT.
On Aug. 29 at 2:30 a.m. EDT (630 UTC), the Moderate Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument that flies aboard NASA’s Aqua satellite used infrared light and found strongest thunderstorms associated with Erin where confined to a small area around the center. There, cloud top temperatures were as cold as minus 50 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 45.5 degrees Celsius). Infrared data provides temperature information, and the strongest thunderstorms that reach high into the atmosphere have the coldest cloud top temperatures.
Storms with colder cloud top temperatures were located far to the north of Erin’s center and are associated with the frontal system of which Erin is merging. Those storms had cloud top temperatures as cold as minus 70 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 56.6 Celsius). Cloud top temperatures that cold indicate strong storms with the potential to generate heavy rainfall.
Read more at NASA / Goddard Space Flight Center
Image: On Aug. 29 at 2:30 a.m. EDT (630 UTC), the MODIS instrument that flies aboard NASA’s Aqua satellite found Erin’s strongest thunderstorms (yellow circle) confined to a small area around the center. Cloud top temperatures were as cold as minus 50 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 45.5 degrees Celsius). Storms with colder cloud top temperatures were located far to the north of Erin’s center and are associated with the frontal system of which Erin is merging. Those storms had cloud top temperatures as cold as minus 70F degrees (minus 56.6C). Cloud top temperatures that cold indicate strong storms with the potential to generate heavy rainfall. Credit: NASA/NRL