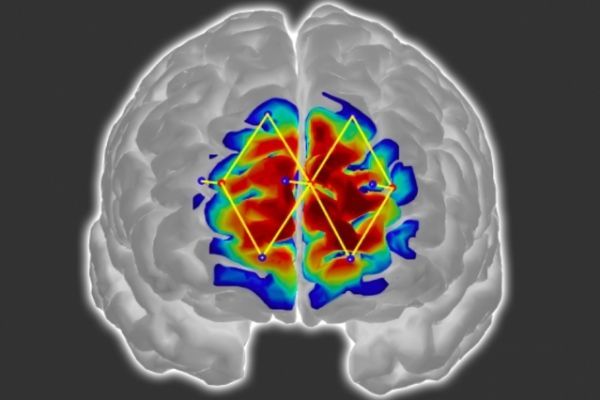
Researchers from MIT and elsewhere have developed a system that measures a patient’s pain level by analyzing brain activity from a portable neuroimaging device. The system could help doctors diagnose and treat pain in unconscious and noncommunicative patients, which could reduce the risk of chronic pain that can occur after surgery.
Pain management is a surprisingly challenging, complex balancing act. Overtreating pain, for example, runs the risk of addicting patients to pain medication. Undertreating pain, on the other hand, may lead to long-term chronic pain and other complications. Today, doctors generally gauge pain levels according to their patients’ own reports of how they’re feeling. But what about patients who can’t communicate how they’re feeling effectively — or at all — such as children, elderly patients with dementia, or those undergoing surgery?
In a paper presented at the International Conference on Affective Computing and Intelligent Interaction, the researchers describe a method to quantify pain in patients. To do so, they leverage an emerging neuroimaging technique called functional near infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS), in which sensors placed around the head measure oxygenated hemoglobin concentrations that indicate neuron activity.
Read more at Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Image: Researchers from MIT and elsewhere have developed a system that detects pain in patients by analyzing brain activity from a wearable neuroimaging device, which could help doctors diagnose and treat pain in unconscious and noncommunicative patients. Courtesy of the researchers, edited by MIT News