Cold cloud top temperatures can tell forecasters if a tropical cyclone has the potential to generate heavy rainfall, and that is exactly what NASA’s Aqua satellite found when it observed the temperatures in Tropical Cyclone Belna over northwestern Madagascar.
One of the ways NASA researches tropical cyclones is using infrared data that provides temperature information. The AIRS instrument aboard NASA’s Aqua satellite captured a look at those temperatures in Belna and gave insight into the storm’s strength.
Cloud top temperatures provide information to forecasters about where the strongest storms are located within a tropical cyclone. Tropical cyclones do not always have uniform strength, and some sides have stronger sides than others. The stronger the storms, the higher they extend into the troposphere, and the colder the cloud temperatures are.
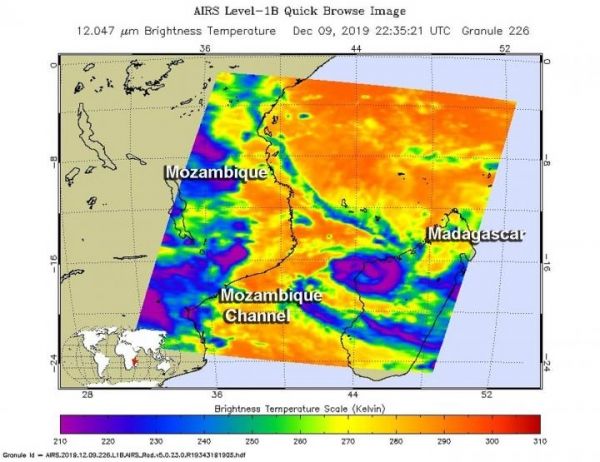
On Dec. 9 at 5:35 p.m. EST (2235 UTC) NASA’s Aqua satellite analyzed the storm using the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument. AIRS found coldest cloud top temperatures as cold as or colder than minus 63 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 53 degrees Celsius) around the center and in a band of thunderstorms east of center over northwestern Madagascar. NASA research has shown that cloud top temperatures that cold indicate strong storms that have the capability to create heavy rain.
Read more at NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center
Image: On Dec. 9 at 5:35 p.m. EST (2235 UTC) NASA's Aqua satellite analyzed Tropical Storm Belna using the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument. AIRS found coldest cloud top temperatures (purple) as cold as or colder than minus 63 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 53 degrees Celsius) around the center and in a band of thunderstorms east of center over northwestern Madagascar. (Credit: NASA JPL/Heidar Thrastarson)