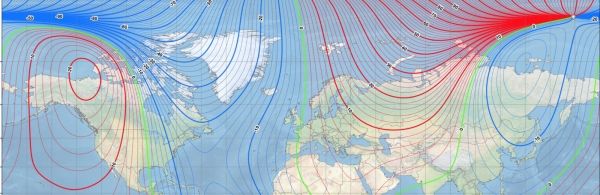
Developed by NCEI and the British Geological Survey, with support from the Cooperative Institute for Research in Environmental Sciences (CIRES), the WMM is a representation of the planet’s magnetic field that gives compasses dependable accuracy.
The WMM now includes “Blackout Zones” around the magnetic poles, as defined by the strength of the horizontal field. Between 2000 and 6000 nanotesla (nT) horizontal field strength is the “Caution Zone” where compasses may start to become prone to errors. The area around the pole between 2000 and 0 nT is the “Unreliable Zone” where compasses may become inaccurate.
Smartphone and consumer electronics companies rely on the WMM to provide consumers with accurate compass apps, maps and GPS services. The WMM is the also the standard navigation tool for the Federal Aviation Administration, U.S. Department of Defense, North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) and more.
A new and updated version of the WMM is released every five years. The WMM2020 model will extend to 2025.
Continue reading at Cooperative Institute for Research in Environmental Sciences
Image via Cooperative Institute for Research in Environmental Sciences