For much of the 2019-2020 austral summer, plumes of bushfire smoke have billowed from southeastern Australia in such large amounts that the ground was barely visible in satellite images. In mid-January, some of those plumes were finally quelled by a few days of much-needed rainfall.
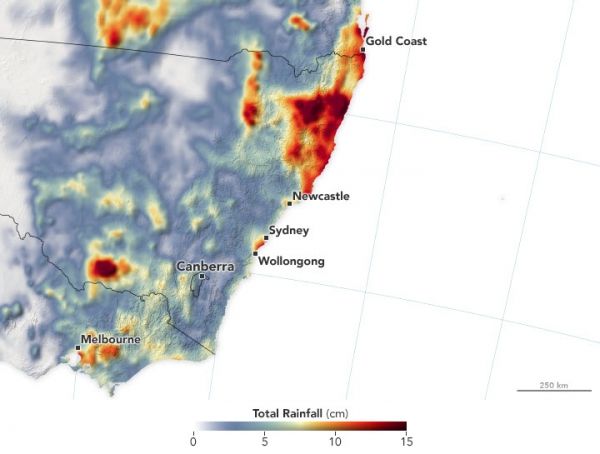
The map above shows rainfall accumulation from January 15-21, 2020, in New South Wales and neighboring states. These data are remotely-sensed estimates that come from the Integrated Multi-Satellite Retrievals for GPM (IMERG), a product of the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) mission. Local rainfall amounts can be significantly higher when measured from the ground.
According to news reports, the largest accumulations in New South Wales occurred north of Sydney, where rainfall averaged between 20 and 30 centimeters (8 and 12 inches). In Victoria, areas near Melbourne received a month’s worth of rain in a single day. The weather system was spotty, however, and some areas along the southeast coast saw less than a centimeter of precipitation.
Continue reading at NASA Earth Observatory
Image via NASA Earth Observatory