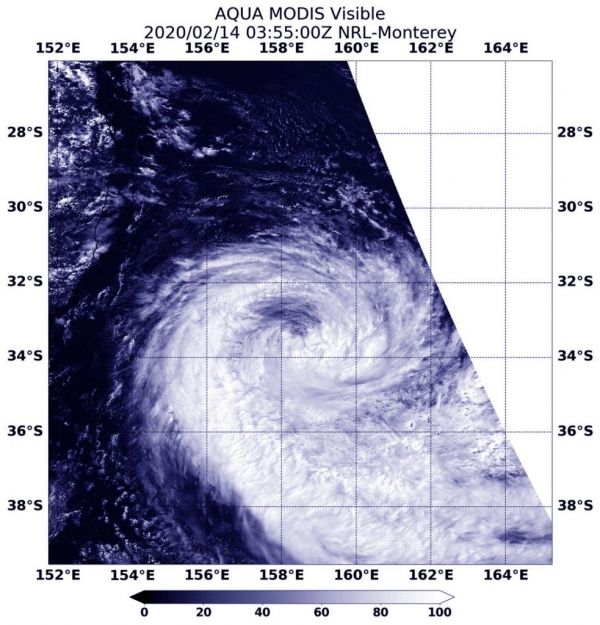
The low-pressure area that had once been Tropical Cyclone Francisco has been lingering in the Southern Indian Ocean since Feb. 6 when it weakened below tropical cyclone status. Since then, Francisco’s remnants moved into an area of warm waters and low wind shear allowing the low-pressure area to re-organize, consolidate and re-form. NASA’s Aqua satellite provided forecasters with a visible image of the zombie storm.
On Feb. 14, the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument that flies aboard NASA’s Aqua satellite provided a visible image that showed the storm had re-developed a rounded shape with bands of thunderstorms spiraling into the low-level center. A more rounded shape of a tropical cyclone indicates it is becoming a more organized storm. Satellite imagery shows a compact system with strong thunderstorms persisting over the low-level circulation. In addition, satellite microwave imagery indicates deep convective banding of thunderstorms over the western semicircle wrapping into the north and east quadrants of a defined low-level circulation center.
On Feb. 14 at 4 a.m. EST (0900 UTC), the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) noted that Francisco’s maximum sustained winds powered back up to 40 knots (46 mph/74 kph). Francisco re-formed near latitude 19.0 degrees south and longitude 49.3 east, approximately 114 nautical miles east of Antananarivo, Madagascar. Francisco has tracked southwestward.
Read more at NASA / Goddard Space Flight Center
Image: On Feb. 14, the MODIS instrument that flies aboard NASA’s Aqua satellite provided a visible image of re-formed Tropical Cyclone Francisco heading for landfall in east-central Madagascar. Credit: NASA/NRL