Air pollution is responsible for shortening people’s lives worldwide on a scale far greater than wars and other forms of violence, parasitic and vector-born diseases such as malaria, HIV/AIDS and smoking, according to a study published in Cardiovascular Research today.
Professors Jos Lelieveld and Thomas Münzel, of the Max Planck Institute for Chemistry and the Department of Cardiology of the University Medical Centre Mainz in Mainz, Germany, who led the research, say the findings suggest the world is facing an air pollution “pandemic”.
Using a new method of modelling the effects of various sources of air pollution on death rates, the researchers estimated that globally air pollution caused an extra 8.8 million premature deaths a year in 2015. This represents an average shortening of life expectancy of nearly three years for all persons worldwide.
In comparison, tobacco smoking shortens life expectancy by an average of 2.2 years (7.2 million deaths), HIV/AIDS by 0.7 years (1 million deaths), diseases like malaria that are carried by parasites or insects such as mosquitoes, ticks and fleas by 0.6 years (600,000 deaths), and all forms of violence (including deaths in wars) by 0.3 years (530,000 deaths).
Read more at European Society of Cardiology
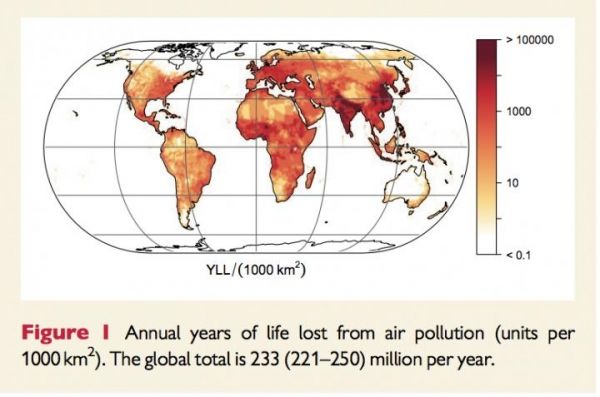
Image: Heat map showing years of life lost each year from air pollution. (Credit: Cardiovascular Research)