The accretion of new material during Pluto’s formation may have generated enough heat to create a liquid ocean that has persisted beneath an icy crust to the present day, despite the dwarf planet’s orbit far from the sun in the cold outer reaches of the solar system.
This “hot start” scenario, presented in a paper published June 22 in Nature Geoscience, contrasts with the traditional view of Pluto’s origins as a ball of frozen ice and rock in which radioactive decay could have eventually generated enough heat to melt the ice and form a subsurface ocean.
“For a long time people have thought about the thermal evolution of Pluto and the ability of an ocean to survive to the present day,” said coauthor Francis Nimmo, professor of Earth and planetary sciences at UC Santa Cruz. “Now that we have images of Pluto’s surface from NASA’s New Horizons mission, we can compare what we see with the predictions of different thermal evolution models.”
Because water expands when it freezes and contracts when it melts, the hot-start and cold-start scenarios have different implications for the tectonics and resulting surface features of Pluto, explained first author and UCSC graduate student Carver Bierson.
Read more at University of California - Santa Cruz
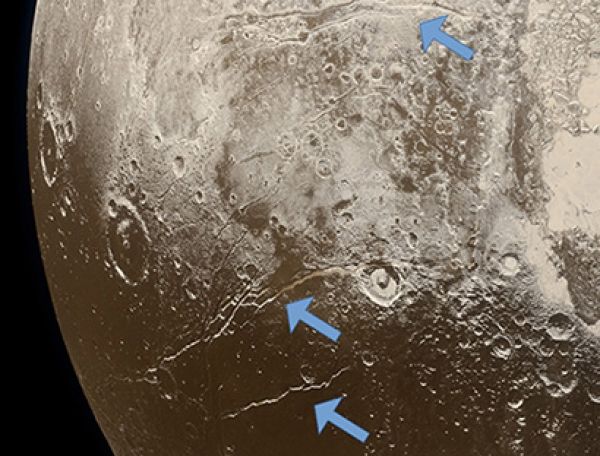
Image: Extensional faults (arrows) on the surface of Pluto indicate expansion of the dwarf planet’s icy crust, attributed to freezing of a subsurface ocean. (Image credit: NASA/Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory/Southwest Research Institute/Alex Parker)