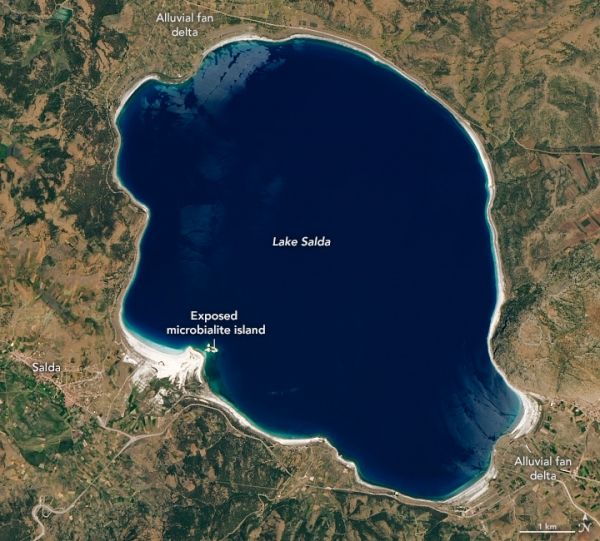
You may not be able to travel to Jezero Crater on Mars, but you can visit the next best thing: Lake Salda, Turkey. Though it is located a world away, Lake Salda shares similar minerology and geology as the dry Martian lakebed.
Researchers are using their understanding of Lake Salda to help guide the Mars 2020 mission, which will drop the Perseverance rover into the crater to search for signs of ancient life. “One of the great things about visiting Lake Salda is it really gives you a sense of what it would have been like to stand on the shores of ancient Lake Jezero,” said Briony Horgan, a planetary scientist at Purdue University and member of the Perseverance science team.
Jezero is a 45-kilometer (28-mile) wide ancient impact crater located in the northwest corner of a larger impact basin on Mars—essentially an impact crater within an impact crater. It is noteworthy because it once contained a lake, as evidenced by delta deposits. Previously, scientists discovered carbonate minerals throughout the crater. Using data taken by NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO), Horgan and her team recently discovered evidence that some of these carbonate minerals may have formed in the lake.
Continue reading at NASA Earth Observatory
Image via NASA Earth Observatory