TESS has discovered 74 exoplanets, or worlds beyond our solar system. Astronomers are sifting through some 1,200 additional exoplanet candidates, where potential new worlds await confirmation. More than 600 of these candidates lie in the northern sky.
TESS locates planets by simultaneously monitoring many stars over large regions of the sky and watching for tiny changes in their brightness. When a planet passes in front of its host star from our perspective, it blocks some of the star’s light, causing it to temporarily dim. This event is called a transit, and it repeats with every orbit of the planet around the star. This technique has proven to be the most successful planet-finding strategy so far, accounting for about three quarters of the nearly 4,300 exoplanets now known. The data collected also allow for the study of other phenomena such as stellar variations and supernova explosions in unprecedented detail.
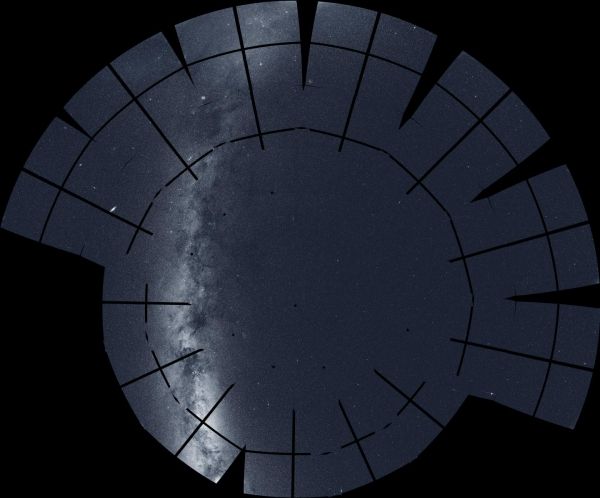
This mosaic of the northern sky incorporates 208 images taken by NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) during its second year of science operations, completed in July 2020. The mission split the northern sky into 13 sectors, each of which was imaged for nearly a month by the spacecraft's four cameras. Among the many notable celestial objects visible: the glowing arc and obscuring dust clouds of the Milky Way (left), our home galaxy seen edgewise; the Andromeda galaxy (oval, center left), our nearest large galactic neighbor located 2.5 million light-years away; and the North America Nebula (lower left), part of a stellar factory complex 1,700 light-years away. The prominent dark lines are gaps between the detectors in TESS's camera system. (Photo Credit: NASA/MIT/TESS and Ethan Kruse (USRA))
Read more: NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center