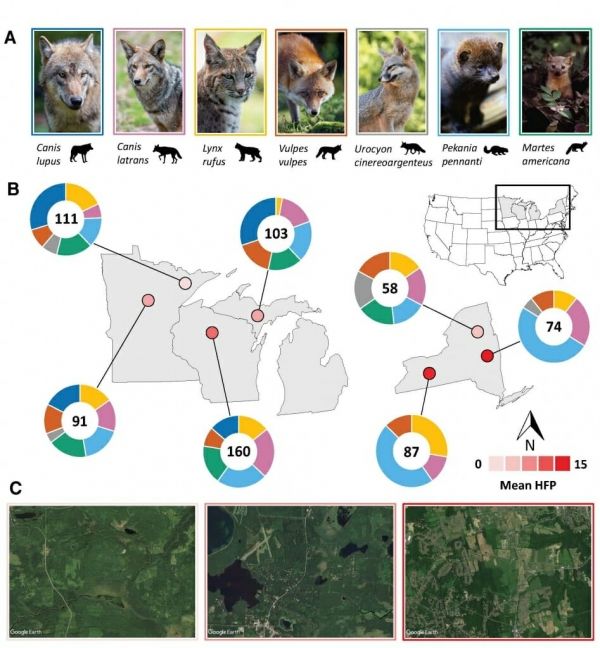
Ecologists at the University of Wisconsin–Madison have found that carnivores living near people can get more than half of their diets from human food sources, a major lifestyle disruption that could put North America’s carnivore-dominated ecosystems at risk.
The researchers studied the diets of seven predator species across the Great Lakes region of the U.S. They gathered bone and fur samples for chemical analysis from areas as remote as national parks to major metropolitan regions like Albany, New York. They found that the closer carnivores lived to cities and farms, the more human food they ate.
While evolution has shaped these species to compete for different resources, their newfound reliance on a common food source could put them in conflict with one another. That conflict could be reordering the relationship between different carnivores and between predators and prey, with an unknown but likely detrimental impact on ecosystems that evolved under significant influence of strong predators.
Continue reading at University of Wisconsin Madison
Image via University of Wisconsin Madison