Got any spaces left on that 2020 bingo card? Pencil in “another Dust Bowl in the Great Plains.” A study from University of Utah researchers and their colleagues finds that atmospheric dust levels are rising across the Great Plains at a rate of up to 5% per year.
The trend of rising dust parallels expansion of cropland and seasonal crop cycles, suggesting that farming practices are exposing more soil to wind erosion. And if the Great Plains becomes drier, a possibility under climate change scenarios, then all the pieces are in place for a repeat of the Dust Bowl that devastated the Midwest in the 1930s.
“We can’t make changes to the earth surface without some kind of consequence just as we can’t burn fossil fuels without consequences,” says Andy Lambert, lead author of the study and a recent U graduate. “So while the agriculture industry is absolutely important, we need to think more carefully about where and how we plant.”
The research is published in Geophysical Research Letters and was funded by the Utah Science Technology and Research (USTAR) initiative, the Global Change and Sustainability Center at the University of Utah, and the Associated Students of the University of Utah.
Read more: University of Utah
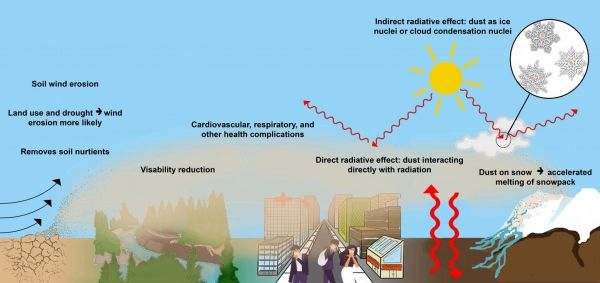
The hazards of increased atmospheric dust. (Photo Credit: Talie Lambert)