The coastline of Israel is one of the warmest areas in the Mediterranean Sea. Here, most marine species have been at the limits of their tolerance to high temperatures for a long time – and now they are already beyond those limits. Global warming has led to an increase in sea temperatures beyond those temperatures that Mediterranean species can sustain. Consequently, many of them are going locally extinct.
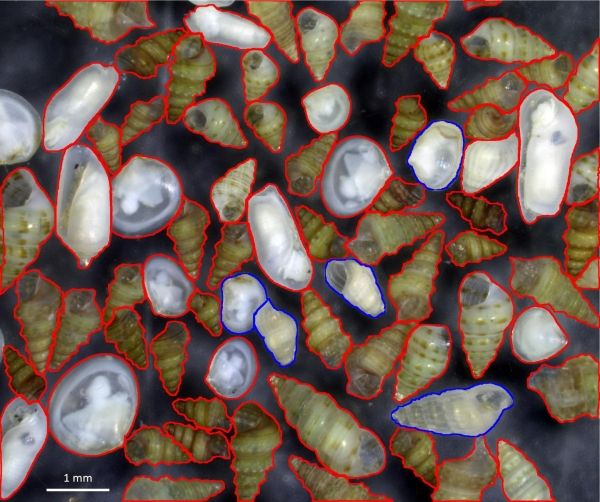
Paolo Albano’s team quantified this local extinction for marine molluscs, an invertebrate group encompassing snails, clams and mussels. They thoroughly surveyed the Israeli coastline and reconstructed the historical species diversity using the accumulations of empty shells on the sea bottom.
Biodiversity loss in the last few decades
The shallow habitats at scuba diving depths are affected most. Here, the researchers were not able to find living individuals of up to 95 per cent of the species whose shells were found in the sediments. The study suggests that most of this loss has occurred recently, presumably in just the last few decades.
Additionally, most of the species still found alive cannot grow enough to reproduce, "a clear sign that the biodiversity collapse will further continue," says Albano. In contrast, the tropical species that enter from the Suez Canal thrive. The warm waters in the Eastern Mediterranean are very suitable habitats for them. Indeed, they occur in large populations and their individuals are fully fit to reproduce.
Read more at University of Vienna
Image: Molluscs of a sample from Southern Israel: in red, those belonging to species of Red Sea origin, in blue, those of Mediterranean origin. Native species are very few, whereas tropical ones are dominant, marking the transformation of the ecosystem. (Credit: © Paolo Albano)