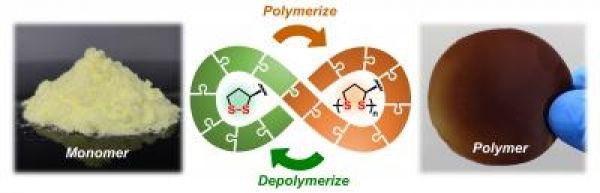
Plastics are among the most successful materials of modern times. However, they also create a huge waste problem. Scientists from the University of Groningen (The Netherlands) and the East China University of Science and Technology (ECUST) in Shanghai produced different polymers from lipoic acid, a natural molecule. These polymers are easily depolymerized under mild conditions. Some 87 percent of the monomers can be recovered in their pure form and re-used to make new polymers of virgin quality. The process is described in an article that was published in the journal Matter on 4 February.
A problem with recycling plastics is that it usually results in a lower-quality product. The best results are obtained by chemical recycling, in which the polymers are broken down into monomers. However, this depolymerization is often very difficult to achieve. At the Feringa Nobel Prize Scientist Joint Research Center, a collaboration between the University of Groningen and ECUST, scientists developed a polymer that can be created and fully depolymerized under mild conditions.
Read more at: University of Groningen
Scientists from the University of Groningen (The Netherlands) and the East China University of Science and Technology (ECUST) in Shanghai produced different polymers from lipoic acid, a natural molecule. These polymers are easily depolymerized under mild conditions. Some 87 percent of the monomers can be recovered in their pure form and re-used to make new polymers of virgin quality. (Photo Credit: Qi Zhang, University of Groningen)