From the Pacific Northwest to the Rocky Mountains, summers in the West are marked by wildfires and smoke. New research from the University of Utah ties the worsening trend of extreme poor air quality events in Western regions to wildfire activity, with growing trends of smoke impacting air quality clear into September. The work is published in Environmental Research Letters.
“In a big picture sense, we can expect it to get worse,” says Kai Wilmot, lead author of the study and doctoral student in the Department of Atmospheric Sciences. “We’re going to see more fire area burned in the Western U.S. between now and in 2050. If we extrapolate our trends forward, it seems to indicate that a lot of urban centers are going to have trouble in meeting air quality standards in as little time as 15 years.”
Many of the West’s inhabitants have seen smoky summer skies in recent years. Last year, dramatic images of an orange-tinted San Francisco Bay Area called attention to the far-reaching problem of wildfire smoke. Wilmot, a native of the Pacific Northwest, has seen the smoke as well and, with his colleagues, looked at trends of extreme air quality events in the West from 2000 to 2019 to see if they correlated with summer wildfires.
Read more at: University of Utah
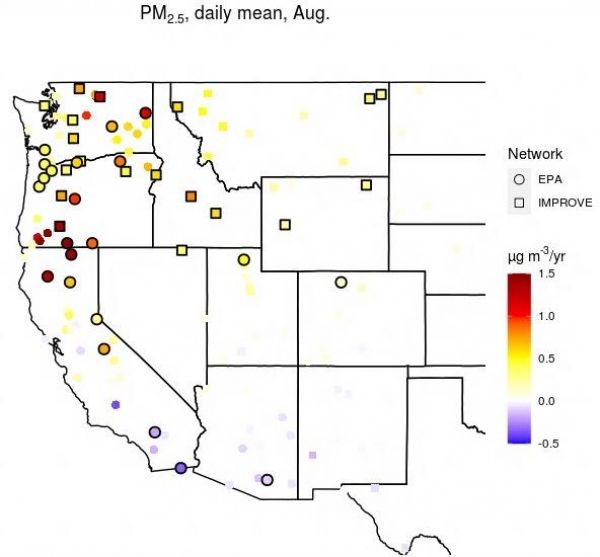
Changes in daily average particulate matter in the month of August from 2000 to 2019. Points outlined in black indicate statistical significance. (Photo Credit: Kai Wilmot)