A filter made from polymer nanothreads blew three kinds of commercial masks out of the water by capturing 99.9% of coronavirus aerosols in an experiment.
“Our work is the first study to use coronavirus aerosols for evaluating filtration efficiency of face masks and air filters,” said corresponding author Yun Shen, a UC Riverside assistant professor of chemical and environmental engineering. “Previous studies have used surrogates of saline solution, polystyrene beads, and bacteriophages — a group of viruses that infect bacteria.”
The study, led by engineers at UC Riverside and The George Washington University, compared the effectiveness of surgical and cotton masks, a neck gaiter, and electrospun nanofiber membranes at removing coronavirus aerosols to prevent airborne transmission. The cotton mask and neck gaiter only removed about 45%-73% of the aerosols. The surgical mask did much better, removing 98% of coronavirus aerosols. But the nanofiber filter removed almost all of the coronavirus aerosols.
The World Health Organization and Centers for Disease Control have both recognized aerosols as a major mechanism of COVID-19 virus transmission. Aerosols are tiny particles of water or other matter that can remain suspended in air for long periods of time and are small enough to penetrate the respiratory system.
Read more at University of California - Riverside
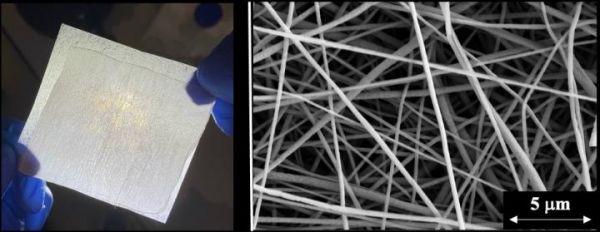
Image: Left: A nanofiber filter that captures 99.9% of coronavirus aerosols; Right: A highly magnified image of the polymer nanofibers. (Credit: Yun Shen)