Astronomers discovered a black hole unlike any other. At one hundred thousand solar masses, it is smaller than the black holes we have found at the centers of galaxies, but bigger than the black holes that are born when stars explode. This makes it one of the only confirmed intermediate-mass black holes, an object that has long been sought by astronomers.
“We have very good detections of the biggest, stellar-mass black holes up to 100 times the size of our sun, and supermassive black holes at the centers of galaxies that are millions of times the size of our sun, but there aren’t any measurements of black between these. That’s a large gap,” said senior author Anil Seth, associate professor of astronomy at the University of Utah and co-author of the study. “This discovery fills the gap.”
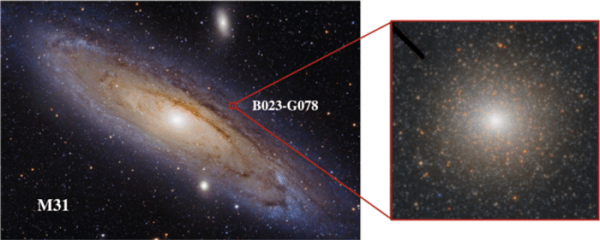
The black hole was hidden within B023-G078, an enormous star cluster in our closest neighboring galaxy Andromeda. Long thought to be a globular star cluster, the researchers argue that B023-G078 is instead a stripped nucleus. Stripped nuclei are remnants of small galaxies that fell into bigger ones and had their outer stars stripped away by gravitational forces. What’s left behind is a tiny, dense nucleus orbiting the bigger galaxy and at the center of that nucleus, a black hole.
“Previously, we’ve found big black holes within massive, stripped nuclei that are much bigger than B023-G078. We knew that there must be smaller black holes in lower mass stripped nuclei, but there’s never been direct evidence,” said lead author Renuka Pechetti of Liverpool John Moores University, who started the research while at the U. “I think this is a pretty clear case that we have finally found one of these objects.”
Read more at: University of Utah
The left panel shows a wide-field image of M31 with the red box and inset showing the location and image of B023-G78 where the black hole was found. (Photo Credit: Iván Éder, https://www.astroeder.com/; HST ACS/HRC)