As carbon dioxide continues to build up in the Earth’s atmosphere, research teams around the world have spent years seeking ways to remove the gas efficiently from the air. Meanwhile, the world’s number one “sink” for carbon dioxide from the atmosphere is the ocean, which soaks up some 30 to 40 percent of all of the gas produced by human activities.
Recently, the possibility of removing carbon dioxide directly from ocean water has emerged as another promising possibility for mitigating CO2 emissions, one that could potentially someday even lead to overall net negative emissions. But, like air capture systems, the idea has not yet led to any widespread use, though there are a few companies attempting to enter this area.
Now, a team of researchers at MIT says they may have found the key to a truly efficient and inexpensive removal mechanism. The findings were reported this week in the journal Energy and Environmental Science, in a paper by MIT professors T. Alan Hatton and Kripa Varanasi, postdoc Seoni Kim, and graduate students Michael Nitzsche, Simon Rufer, and Jack Lake.
Read more at Massachusetts Institute of Technology
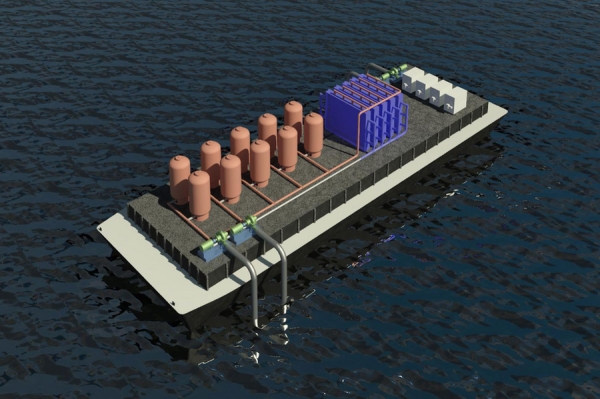
Image: Researchers have found an effective new method for removing greenhouse gas from the ocean. The new method could be implemented by ships, processing water as they travel, or at locations such as offshore drilling platforms or at aquaculture fish farms. Credits: Courtesy of the researchers