The discovery could expand scientific understanding of fire histories to arid regions around the world.
Knowing how the frequency and intensity of wildfires has changed over time offers scientists a glimpse into Earth’s past landscapes, as well as an understanding of future climate change impacts. To reconstruct fire records, researchers rely heavily on sediment records from lake beds, but this means that fire histories from arid regions are often overlooked. Now, a new study shows that sand dunes can serve as repositories of fire history and aid in expanding scientific understanding of fire regimes around the world.
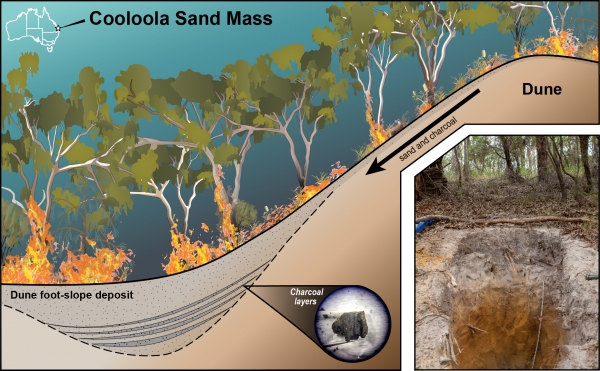
Published May 11 in Quaternary Research, the study is the first to examine sedimentary records preserved in foot-slope deposits of sand dunes. The research team, led by Nicholas Patton, Ph.D., a postdoctoral researcher now at DRI, studied four sand dunes at the Cooloola Sand Mass in Australia. Australia is one of the world’s most fire-prone landscapes, with a long history of both natural and cultural burning, and vast expanses without lakes or ponds to gather sedimentary records from. The researchers aimed to prove that these sand dune deposits could be used to reconstruct reliable, multi-millennial fire histories. These previously unrecognized archives could potentially be used in arid regions around the world to fill knowledge gaps in places where fire shapes the landscape.
“Many fire and paleoclimate records are located where there’s a lot of water bodies such as lakes, peats, and bogs,” Patton says. “And because of this, most global models really have a bias towards temperate regions.”
Read more at Desert Research Institute
Image: An illustration showing how charcoal layers accumulate in dune foot-slope deposits. (Credit: Nicholas Patton/DRI)