Researchers in Israel have discovered that breast tumors can boost their growth by recruiting stromal cells originally formed in the bone marrow. The study, which will be published November 23 in the Journal of Experimental Medicine, reveals that the recruitment of bone marrow–derived fibroblasts lowers the odds of surviving breast cancer, but suggests that targeting these cells could be an effective way of treating the disease.
Within solid tumors, cancer cells are surrounded by other cell types that, though not cancerous themselves, boost tumor growth and metastasis. Breast tumors, for example, contain large numbers of fibroblast cells that promote cancer cell proliferation, inflammation, and the formation of new blood vessels to supply the growing tumor with nutrients and oxygen. Many of these cancer-associated fibroblasts are derived from the neighboring breast tissue, but others seem to come from elsewhere in the body.
Neta Erez and colleagues at the Sackler School of Medicine, Tel Aviv University, discovered that, in mice with breast cancer, a significant number of cancer-associated fibroblasts are derived from bone marrow cells called mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs). The researchers found that breast tumors can recruit MSCs from the bone marrow and cause them to develop into fibroblasts.
Read more at Rockefeller University Press
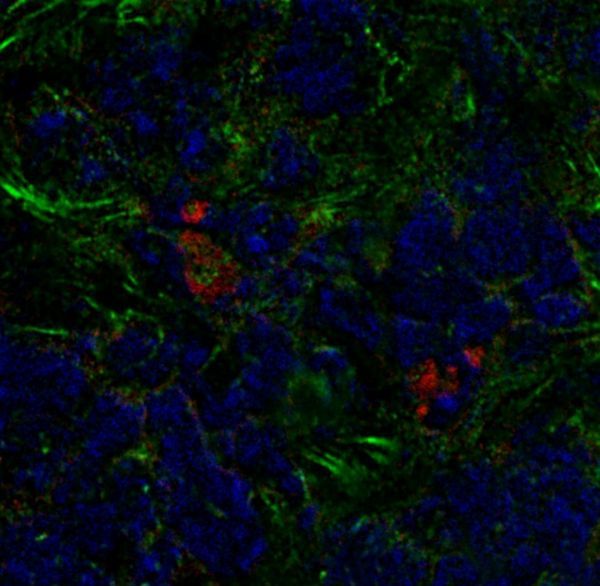
Image: A mouse breast tumor contains bone marrow-derived fibroblasts (red) as well as other cancer-associated fibroblasts (green). (Credit: Raz et al., 2018)