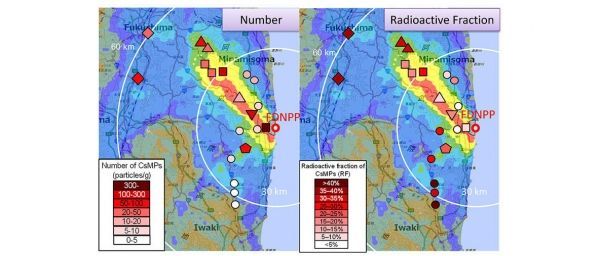
A new method allows scientists to create a quantitative map of radioactive cesium-rich microparticle distribution in soils collected around the damaged Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. This could help inform clean-up efforts in Fukushima region.
A large quantity of radioactivity was released into the environment during the 2011 Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident. The released radioactivity included small, poorly soluble, cesium-rich microparticles. The microparticles have a very high radioactivity per unit mass (~1011 Bq/g), but their distribution, number, source, and movement in the environment has remained poorly understood. This lack of information has made it hard to predict the potential impact of the radioactive microparticles.
However, a study just published in the scientific journal Chemosphere, involving scientists from Japan, Finland, France, and the USA, addresses these issues. The team, led by Dr. Satoshi Utsunomiya, Ryohei Ikehara, and Kazuya Morooka (Kyushu University), developed a method in 2018 that allows scientists to quantify the amount of cesium-rich microparticles in soil and sediment samples.
They have now applied the method to a wide range of soil samples taken from within, and outside, the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear exclusion zone, and this has allowed them to publish the first quantitative map of cesium-rich microparticle distribution in parts of Fukushima region.
Continue reading at University of Helsinki
Image via University of Helsinki