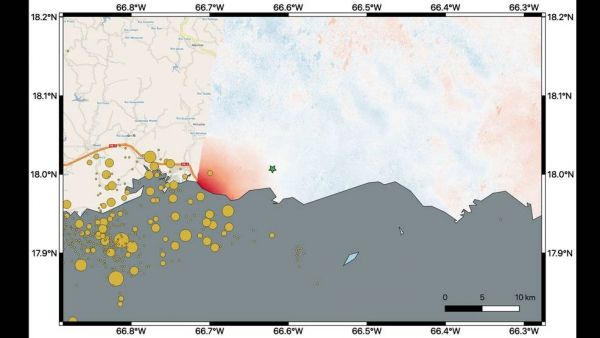
NASA scientists are using satellite data to help federal and local agencies identify areas with potential damage. Earthquakes cause permanent changes to the ground surface. By comparing interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR) data acquired on Jan. 9, 2020, with data acquired on Dec. 28, 2019, from the Copernicus Sentinel-1A satellite, the scientists were able to map where, how much and in what direction those changes occurred.
Managed by the European Space Agency (ESA), the Copernicus Sentinel-1A satellite was able to see the eastern two-thirds of the island during the Jan. 9 flyover. On the map, red indicates areas where the ground was changed, or displaced, with darker shades corresponding to more significant displacement. The scientists found that the greatest displacement from the flyover area occurred west of the city of Ponce (identified by the green star), not far from the quake's offshore epicenter. They recorded up to 5.5 inches (14 centimeters) of ground change there. The ground appeared to shift downward and slightly to the west.
The quake epicenter and the cluster of quakes and aftershocks in the region identified by the United States Geological Survey (shown as orange circles) fall just west of the satellite's Jan. 9 track. Because of this, scientists also plan to analyze data from Sentinel-1A's forthcoming Jan. 14 flyover, which will include western Puerto Rico.
Continue reading at NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory
Image via NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory