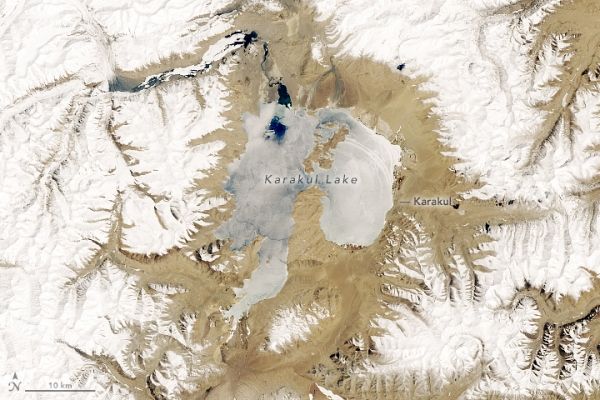
Karakul in many Turkish languages means “black lake.” That description of Karakul Lake, located high in the eastern Pamir Mountains in Tajikistan, is accurate for some of the year. But during the region’s frigid winter, the dark surface is exchanged for a layer of bright white.
The seasonal snow and ice cover had not yet melted by May 1, 2019, when the Operational Land Imager (OLI) on Landsat 8 acquired these images. Areas of open water are starting to appear as the air temperatures in May start to climb to around 13.8 degrees C (57 degrees F)—far warmer than the average January temperature of 5 degrees F.
The wide view (second image) shows some of the nearby snow-covered mountains and glaciers. Meltwater from this snow and ice is an important source of freshwater for the high-mountain lake, which receives very little rainfall—less than 3 centimeters per year. Without any rivers draining the lake, water loss occurs primarily through evaporation. As a result, the lake is saltier than ocean water, or “hypersaline.”
Continue reading at NASA Earth Observatory
Image via NASA Earth Observatory